Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Enhances generation by retrieving relevant documents before producing responses
Augmented Generation represents a family of techniques that enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) with external data, knowledge, and processing capabilities. These approaches address core limitations of standalone LLMs by providing reliable, up-to-date information and domain-specific knowledge.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Enhances generation by retrieving relevant documents before producing responses
Context-Augmented Generation (CAG)
Dynamically identifies relevant context to include during generation
Tool-Augmented Generation (TAG)
Integrates specialized tools and APIs to extend capabilities
Knowledge Graph Augmentation
Leverages structured knowledge repositories for factual grounding
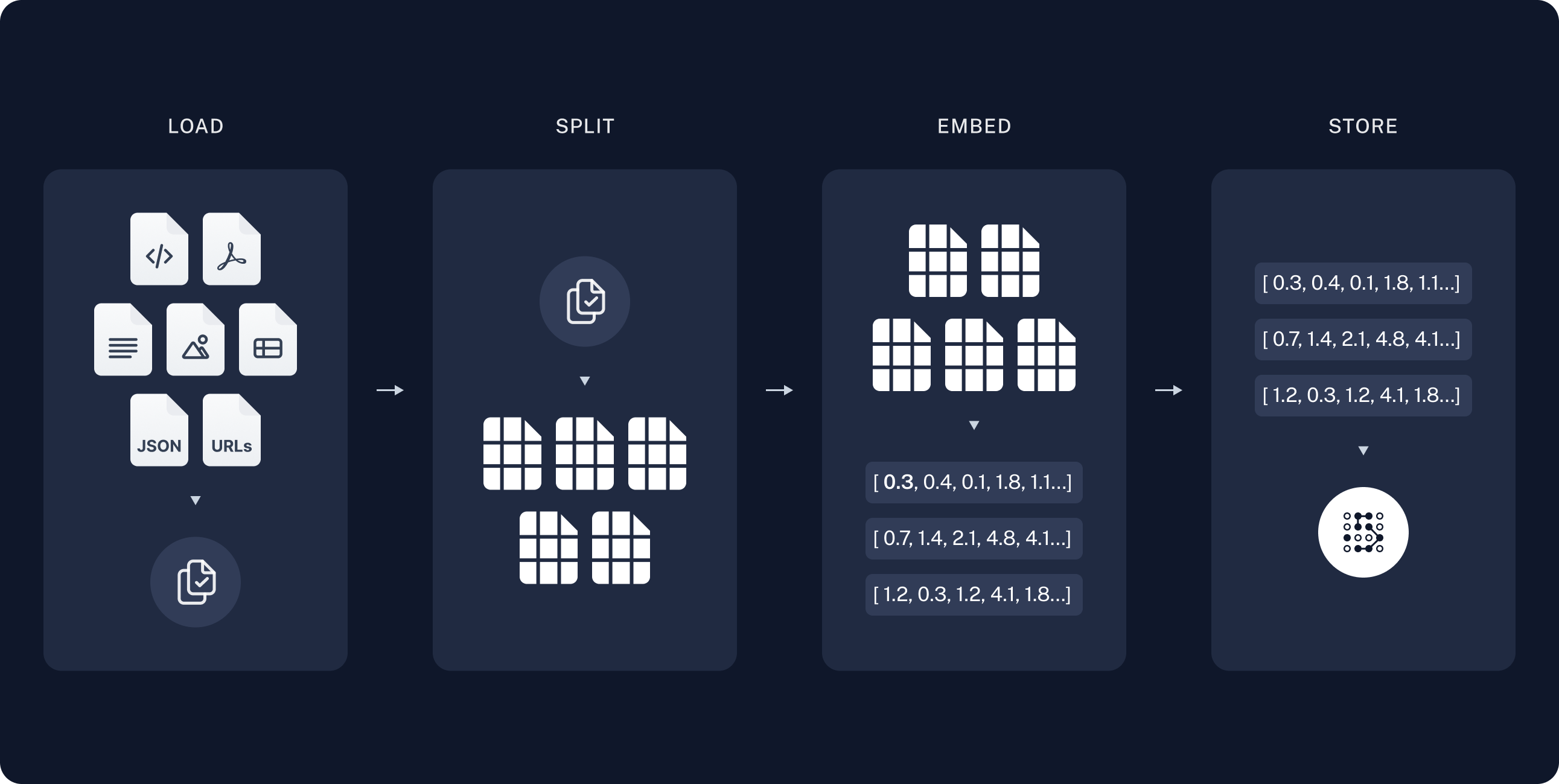
RAG combines information retrieval with text generation to produce outputs grounded in specific knowledge sources.
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQAfrom langchain.vectorstores import Chromafrom langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddingsfrom langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Create vector store from documents
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents, embeddings)
# Create RAG chain
rag_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=OpenAI(),chain_type="stuff",retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever())
# Query the system
response = rag_chain.run("What is the capital of France?")from langchain.retrievers import SelfQueryRetrieverfrom langchain.chains import RetrievalQAfrom langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# Create a self-query retriever that can understand the query intentretriever = SelfQueryRetriever.from_llm( llm, vectorstore, document_content_description="Company knowledge base documents")
# Custom prompt that formats the retrieved documentscustom_prompt = PromptTemplate( template="""Answer the question based only on the following context: {context}
Question: {question} Answer: """, input_variables=["context", "question"])
# Advanced RAG chain with custom promptadvanced_rag = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type( llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=retriever, chain_type_kwargs={"prompt": custom_prompt})RAG implementations vary in complexity and approach based on specific use cases. We utilize three primary RAG architectures:
Vector RAG
The foundational RAG implementation using vector embeddings and similarity search
Graph RAG
Enhanced RAG leveraging graph structures to capture relationships between entities
Agentic RAG
Advanced RAG with autonomous decision-making and workflow optimization
Vector RAG converts queries and documents into high-dimensional vector embeddings, then retrieves the most relevant information using similarity search techniques like cosine similarity.


Graph RAG structures knowledge as a graph where nodes represent entities and edges define their relationships, capturing contextual and hierarchical connections that Vector RAG cannot.
Agentic RAG extends beyond basic retrieval by integrating autonomous decision-making, workflow optimization, and iterative refinement capabilities.

# Example of Agentic RAG implementationfrom langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agentfrom langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemoryfrom langchain.tools import Tool
# Define retrieval toolsvector_search = Tool( name="vector_search", description="Search for relevant documents using vector similarity", func=lambda query: vector_db.search(query))
knowledge_graph = Tool( name="knowledge_graph", description="Query the knowledge graph for related entities", func=lambda entity: graph_db.get_related_entities(entity))
# Create agent with toolsagent = create_react_agent( llm=llm, tools=[vector_search, knowledge_graph], verbose=True)
# Configure agent executor with memoryagent_executor = AgentExecutor.from_agent_and_tools( agent=agent, tools=[vector_search, knowledge_graph], memory=ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True), verbose=True)
# Execute agentic RAG queryresult = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "What treatments are effective for condition X?"})In our most advanced implementations, we combine Vector RAG, Graph RAG, and Agentic approaches to create hybrid systems that leverage:
CAG focuses on dynamically identifying and incorporating the most relevant context during generation, often including:
def generate_with_context(query, user_history, profile_data, current_session): # Identify relevant context elements relevant_history = filter_relevant_interactions(user_history, query) applicable_preferences = extract_preferences(profile_data, query) session_context = summarize_session(current_session)
# Assemble context prompt context = f""" User query: {query}
Relevant past interactions: {relevant_history} User preferences: {applicable_preferences} Current session context: {session_context} """
# Generate response with assembled context response = llm.generate(context)
return responseFLARE is an advanced augmentation technique that enables LLMs to:
Self-Reflection
Enables models to identify uncertainty in their own outputs
Forward Verification
Checks information before completing generation
def flare_generation(query): # Generate initial response with uncertainty markers initial_response = llm.generate(query, max_tokens=50)
# Extract uncertainties and queries requiring verification verification_points = extract_uncertainty_points(initial_response)
# Verify each point using external tools/knowledge verified_info = {} for point in verification_points: verified_info[point] = knowledge_base.verify(point)
# Complete generation with verified information final_response = llm.generate( query, initial_response, verified_info, continue=True )
return final_response| Technique | Strengths | Best Use Cases | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAG | Document grounding, Factual accuracy | Knowledge-intensive applications, Customer support | Medium |
| CAG | Personalization, Continuity | Conversational agents, User-specific services | Medium-High |
| TAG | Specialized capabilities, Real-time data | Multi-step tasks, Data analysis | High |
| FLARE | Self-verification, Reasoning | Critical applications, Scientific domains | Very High |
In our client solutions, we often implement multiple augmentation techniques in tandem:
We implemented a RAG-based system with specialized financial knowledge:
Combined RAG with FLARE for medical information verification:
The field of augmented generation continues to evolve rapidly. We’re actively researching:
As these technologies mature, the gap between general-purpose LLMs and specialized expert systems will continue to narrow, enabling more reliable and capable AI solutions across domains.
Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG) is a technique that improves LLM performance and efficiency by storing and reusing previous generation results. Unlike RAG which focuses on retrieving external documents, CAG leverages the model’s own past outputs.
Response Caching
Stores frequently requested information and responses for rapid retrieval
Computation Reuse
Saves computational resources by avoiding redundant generation
Consistency
Ensures uniform responses to similar queries over time
from vector_store import VectorCachefrom langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Initialize cache and LLM
cache = VectorCache(embedding_dimension=1536)llm = OpenAI()
def generate_with_cache(query): # Check cache for similar queriescache_hit, cached_response = cache.lookup(query, threshold=0.92)
if cache_hit: return cached_response
# Generate new response if not in cache new_response = llm.generate(query)
# Update cache with new response cache.store(query, new_response)
return new_responseimport timefrom langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddingsfrom langchain.vectorstores import FAISSfrom langchain.llms import OpenAI
class AdvancedCAG: def __init__(self): self.embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings() self.cache = FAISS.from_texts([], self.embeddings) self.llm = OpenAI() self.ttl = 86400 # Time-to-live: 24 hours self.cache_metadata = {}
def generate(self, query, force_refresh=False): query_vector = self.embeddings.embed_query(query)
if not force_refresh: # Search for similar cached queries similar_docs = self.cache.similarity_search_by_vector( query_vector, k=1, fetch_k=3 )
if similar_docs and len(similar_docs) > 0: doc = similar_docs[0] cache_id = doc.metadata.get('id')
# Check if cache is still valid if cache_id in self.cache_metadata: timestamp = self.cache_metadata[cache_id].get('timestamp') if time.time() - timestamp < self.ttl: # Adapt the cached response if needed return self.adapt_response(doc.page_content, query)
# Generate new response new_response = self.llm.generate(query)
# Store in cache cache_id = str(hash(query + new_response)) metadata = {"id": cache_id, "timestamp": time.time()}
self.cache.add_texts([new_response], [metadata]) self.cache_metadata[cache_id] = metadata
return new_response
def adapt_response(self, cached_response, new_query): # Customize cached response for the new query context # This could involve minor modifications to make it more relevant prompt = f"Adapt this response:\n{cached_response}\nto better answer this query:\n{new_query}" return self.llm.generate(prompt, max_tokens=100)CAG offers several advantages in production environments:

While both techniques augment LLM capabilities, they serve different purposes and can be used together:
| Feature | Cache-Augmented Generation | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Previous model outputs | External knowledge sources |
| Purpose | Performance optimization | Knowledge enhancement |
| Updates | Requires cache invalidation | Immediate with knowledge updates |
| Use Case | Repeated similar queries | Knowledge-intensive applications |