Understanding AI Agents
The concept of AI agents is one of the most discussed topics in the field of artificial intelligence, particularly in the context of Large Language Models (LLMs). While definitions vary across the industry, we can approach this concept from a technical perspective:
The Spectrum of Agency
Rather than debating what qualifies as a “true” AI agent, it’s more productive to think about AI systems on a spectrum of agency. Similar to how autonomous vehicles have different levels of autonomy, AI systems can exhibit varying degrees of agentic behavior.
Levels of Agentic Behavior
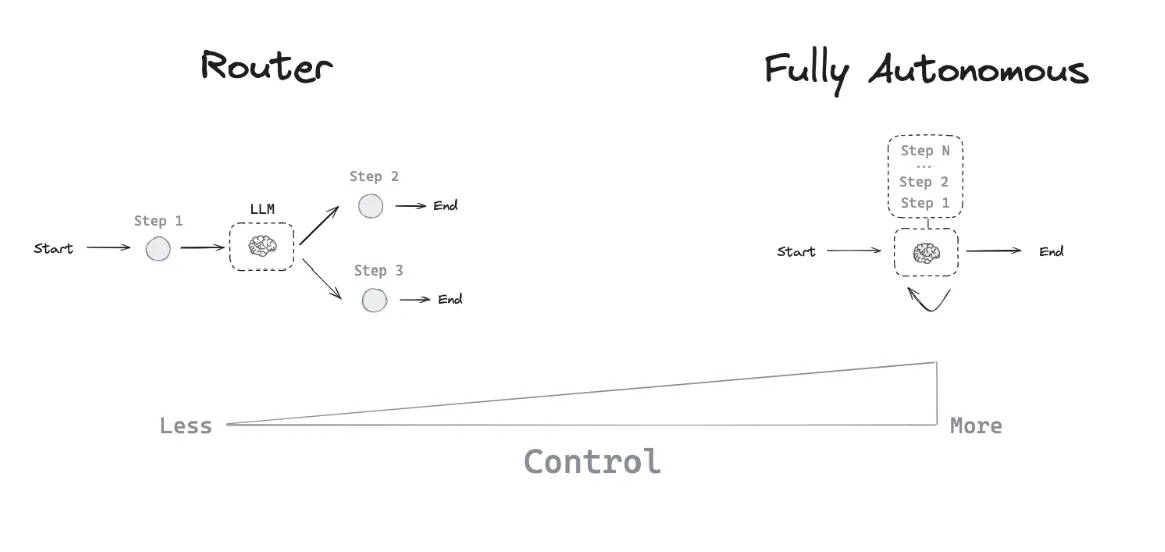
-
Router Level
- Basic routing of inputs to specific workflows
- Minimal autonomous decision-making***
- Single-step LLM-based routing
-
Multi-Router Level
- Multiple routing steps using different LLMs
- Increased complexity in decision trees
- More sophisticated workflow management
-
State Machine Level
- Ability to maintain and manage state
- Loop control (continue or finish decisions)
- More complex decision-making patterns
-
Autonomous Agent Level
- Tool creation and management
- Memory and learning capabilities
- Advanced reasoning and decision-making
- Self-improving capabilities
What Makes a System “Agentic”?
A system becomes more “agentic” as it gains greater autonomy in deciding its behavior. Here are key characteristics that contribute to a system’s agency:
-
Decision-Making Autonomy
- The extent to which the LLM controls the application flow
- Ability to make independent choices
- Complexity of decisions it can handle
-
Tool Interaction
- Capability to use and manage tools
- Understanding of tool capabilities
- Ability to choose appropriate tools for tasks
-
Memory and Learning
- Retention of previous interactions
- Learning from past experiences
- Adaptation of behavior based on history
-
Goal-Oriented Behavior
- Understanding of objectives
- Planning capabilities
- Ability to adjust strategies
Technical Implementation Considerations
When implementing AI agents, several key factors need to be considered:
# Example of a basic routing agentclass SimpleRoutingAgent: def __init__(self, llm): self.llm = llm
def route_request(self, input_query): # LLM decides the routing based on input routing_decision = self.llm.predict( prompt=f"Determine appropriate route for: {input_query}" ) return self.execute_routing(routing_decision)Best Practices
- Start with clear objectives and use cases
- Implement proper error handling and fallbacks
- Monitor and log agent decisions
- Maintain clear boundaries of autonomy
- Implement safety measures and controls
Future Perspectives
As LLM technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see:
- More sophisticated levels of agency
- Better tools for measuring and quantifying agency
- Improved frameworks for building agentic systems
- Enhanced safety and control mechanisms
